Whether fracturing a formation or not must be answered before further step acquired. A comprehensive evaluation on the formation and fluid characteristic is important. Skin build-up evaluation behind casing must be assessed. Sometimes, the fracturing program has been planned before the well is drilled.
Many fracturing techniques have been developed. The fracturing fluid, additives, proppant are varied depend on formation characteristic. Some companies use gel fluid for better fracturing and others combine the fracturing fluid with acid. Make sure no precipitation during acidizing.
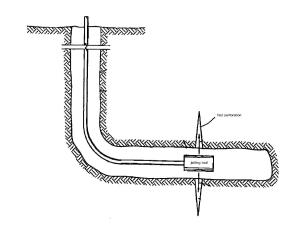
Figure 1: Perforate First Zone
Isolation in multi-zone fracturing is an issue during the fracturing operation. After fracturing the first zone, high fluid loss into the first zone is encountered during fracturing second zone. Some companies use a bridge plug to isolate the first zone and open the bridge plug subsequently after fracturing the second zone. It is not easy to do so in high deviated wells or horizontal wells.
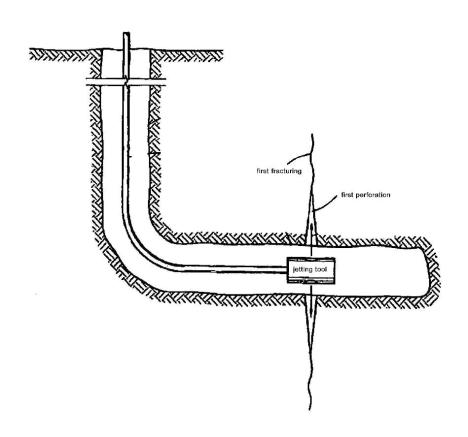
Figure 2: Frac First Zone
In Figure 1, the first zone is perforated by using a jetting tool. Jetting tool perforation is more preferably than shaped charge perforation for some reasons:
1. Jetting tool perforation can reach deeper penetration.
2. Jetting tool perforation can make slot or helical perforation instead of hole only.
3. Jetting tool can directly deliver fracturing fluid for fracturing.
4. Jetting tool can deliver isolation fluid to isolate fractured zone.
5. Jetting tool can do the same procedures on other zone without any trip.

Figure 3: Isolate First Zone
Subsequently after perforating the first zone, the zone is fractured (Figure 2) by using the jetting tool. Optionally, acid can be mixed with the fracturing fluid to etch the formation or do acidizing separately after fracturing. Another additive can be added to fracturing fluid for additional purposes such as corrosion inhibitor, scale inhibitor or paraffin depressant.

Figure 4: Perforate and Fracture Second Zone
In Figure 3, the first zone is isolated by using a viscoelastic surfactant. Viscoelastic surfactant is more preferably as isolation fluid since the fluid can decrease formation damage, more stable against shear and no substantial viscosity loss due to temperature increase. By isolating the first zone, there is no fluid loss during any operation on the second zone.
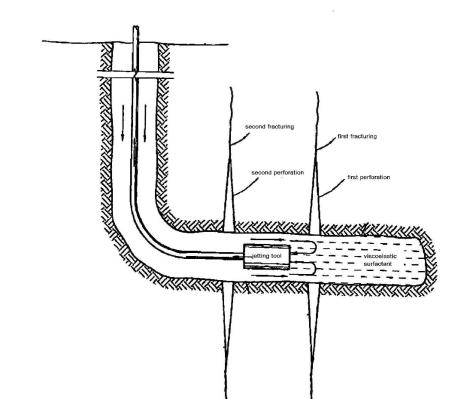
Figure 5: Unloading the well
Perforating and fracturing or any other treatments can be repeated on the second zone (Figure 4). If there is no other zone to be perforated or fractured, the viscoelastic surfactant is unloaded by means of circulation or reverse circulation (Figure 5). If the reservoir pressure is strong enough, the well can be flowed back through the jetting tool or help the well to flow-back by decreasing the hydrostatic fluid within the well using Nitrogen.
Filed under: Drilling & Completion, Production & Operation | Tagged: extended perforation, fracturing, hidraulic fracturing, horizontal completion, hydrajet, openhole, paten, patent, slotted liner, Stimulation, surfactant, viscoelastic surfactant | Leave a comment »

